Outline offers a bird's eye view; Numbers and Labels show hotlinks you can click to Jump to, or right click to Copy Link to; Numbers show where you are. Learn more.
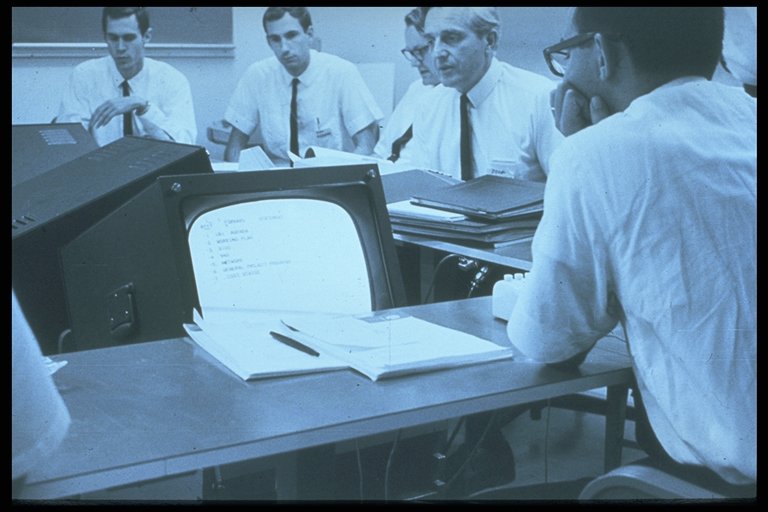
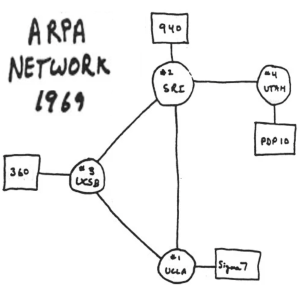
By 1965 Bob Taylor found himself directing ARPA's IPTO, and soon turned his attention to making computer networking a reality, recruiting colleague Larry Roberts to manage the effort. They decided to begin by first networking the computers in the labs ARPA was funding, and expand from there. In 1967 Bob Taylor announced his plans at a meeting of his Principal Investigators. There were many skeptics around that table, but Doug Engelbart was absolutely thrilled – 'networking' would dovetail beautifully into his research agenda, and he offered on the spot to host an online information center to support the network user community. And so Doug Engelbart's lab was among the first selected for the initial beta installation of the ARPANET, along with UCLA, University of Utah, and UC Santa Barbara. In 1968, Bolt, Beranek and Newman (BBN) won the bid to develop the underlying network technology for the ARPANET – a smallish computer (the size of a refrigerator) called an Interface Message Processor, or IMP, to be installed at every host site to form the network, linking in the host computer(s). Representatives from the four beta host sites, including Doug's chief architect Jeff Rulifson, began meeting in the summer of 1968 to hash out the details and protocols for participation, ably led by UCLA's Steve Crocker. Thus the Network Working Group was born (RFC#1). See Retrospectives below to watch Bob Taylor and Vint Cerf recall these early beginnings. By years' end, with preliminary plans for the ARPANET now in motion, Doug announced his participation during his session at the 1968 Fall Joint Computer Conference, which lucky for us was filmed(!) -- this session later became known as the "Mother of All Demos." On October 1, 1969 Doug and his team again presented their work in a conference session, in live demonstration format, this time with much more to say about the imminent ARPANET and their planned participation. See Watch Doug & Others below for select footage from his 1968 and 1969 demo presentations. 2nd Host receives 1st Transmission 2
The ARPANET went live the following year on October 29, 1969. The first two sites to come online were Len Kleinrock's lab at UCLA, and Doug Engelbart's Augmentation Research Center at SRI. At each site an IMP was installed to interface the onsite host computer with the network, which required some programming at both ends. When it came time to test transmission over the network between the two sites, the task fell to two young programmers – Bill Duvall in Doug's lab at SRI in Menlo Park, CA, and Charlie Kline at UCLA, in Los Angeles, CA. On October 29, 1969, the world's first electronic computer network, the ARPANET, was established between nodes at Leonard Kleinrock's lab at UCLA and Engelbart's lab at SRI. Interface Message Processors at both sites served as the backbone of this first [network]"[2]. The first message sent between them was to be "log" from UCLA to SRI, and "in" from SRI to UCLA ("login") but the computer crashed after the first two letters so the first message between computers was simply "lo". The glitch was soon corrected, and by year's end two more labs were brought online[2]. Watch Bill and Charlie tell their story under Retrospectives below.
The NIC 3The UCLA team had been tasked with running a Network Measurement Center for the ARPANET to monitor network performance, while Engelbart's team was tasked with running a Network Information Center (NIC) to support the ARPANET user community. Through the NIC, ARPANET users would access information about the network, the hosts, fellow users, and the resources available, as well as tools for navigating the information. Doug's lab set to work extending NLS provisions for community support, as well as information system support services which included integrated hyper-email and an automated online publish-retrieve facility called the "Journal".[3]
The year 1972 was a turning point for both the ARPANET and the NIC. In 1972, BBN's Bob Kahn spearheaded a public demonstration of the ARPANET, which now boasted 29 IMPs online, with more in the pipeline. The demonstration would be held at the first International Conference on Computer Communications in Washington, D.C. Doug recruited Elizabeth "Jake" Feinler from SRI's internal Library Research Services to begin developing an ARPANET Resource Handbook to be showcased at the demonstration. Jake worked closely with Doug's team, with the Network Working Group, and others to develop the handbook and much more. The ARPANET was taking off, and the Network Information Center right along with it. Soon BBN released the first 'killer app' – e-mail, which really ignited the ARPANET user base. By 1974 the NIC was funded as a separate project, with Jake as its Principal Investigator. The NIC grew and evolved under her leadership until 1991 when, having grown beyond ARPA's purview, what had originally launched as the ARPANET Network Information Center was transferred to Network Solutions in Virginia, where it became the InterNIC. Watch Jake Feinler recount the NIC beginnings and growth under Retrospectives below. By 1978 there were over 70+ nodes on the ARPANET, interfacing even more host computers. Among them were 5-6 mainframes running NLS, remotely accessed by dozens of end-user organizations, including ARPA's Information Processing Techniques Office: I knew Doug Engelbart and made heavy use of his oNLine System (NLS) to compose documents and to share them through the Network Information Center that was From ARPANET to Internet 4
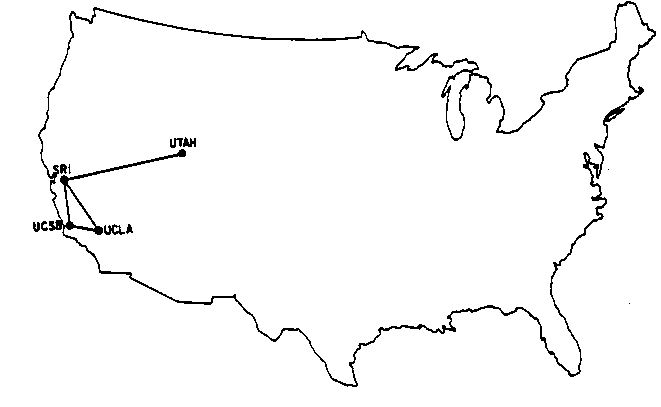
In the Fall of 1972, when BBN's Bob Kahn staged the first public demonstration of the ARPANET, there were 29 nodes on the ARPANET and counting. See Exhibits below to watch the fabulous 1972 documentary produced for that demonstration, touting the wonders of computer networking. Click the map at right to watch the ARPANET grow. Soon more networks were springing up, such as the commercially-available Telenet and Tymnet. Each operated in isolation of the other, as yet there were no provisions for communicating between networks. The Internet emerged from the ARPANET program as an architecture for internetworking, among any number of networks, to allow any host in a network to communicate with any host on any other network. It was Bob Kahn and Vint Cerf who primarily spearheaded that effort in 1973. Bob Kahn was now at ARPA, and Vint Cerf, formerly one of Len Kleinrock's graduate students on the ARPANET launch team at UCLA, was now at Stanford. Bob approached Vint to see about solving the network silos issue. Out of this collaboration emerged TCP/IP protocols for internetworking, which earned Bob and Vint the joint title "Father of the Internet," and numerous awards for their visionary work. Watch Vint Cerf's brief history of the ARPANET/Internet (at right), beginning with J.C.R. Licklider coming to ARPA and meeting Doug Engelbart. More under Retrospectives below.
Watch Doug & Others 5Watch selected archive footage from the time of the 1969 launch of the ARPANET, showing Doug and team presenting their research goals, results and activities in a live demo format. In 1968 Watch Doug and team from his Augmented Human Intellect Research Center (AHIRC) presenting at the Fall Joint Computer Conference in December 1968:
In 1969 Watch Doug and his team presenting at the ASIS Conference on Information Science in October 1969, just 28 days before the first ARPANET transmission:
In 1972 The 1972 ARPANET documentary, titled "Computer Networks - The Heralds Of Resource Sharing," was produced for showing at the 1972 public demonstration of the ARPANET held at the first International Conference on Computer Communications in Washington, D.C. The documentary features interviews with JCR Licklider, Larry Roberts, Bob Kahn, and more, including Dick Watson from Doug's Lab:
Retrospectives Watch selected footage from two interviews by NY Times' John Markoff, the first with Bob Taylor at the 2008 Engelbart and the Dawn of Interactive Computing symposium at Stanford, and the other in 1999 with Doug's team members Bill Duvall, Bill English, and Doug Engelbart in Markoff's "White Rabbit" interview series:
Some of the most creative minds in our field were gathered in Doug's laboratory to explore the augmentation of human intellect through the use of computers. […] NLS was a prototype for what came 20 years later in the form of the World Wide Web although it may be fair to say that Doug's vision and even the functionality of NLS exceeded in some ways what has been accomplished with the Web. Doug's Forward Vision 6
Most histories and timelines of computer networking recount the evolution of the technology, and the expansion of nodes and networks. Doug Engelbart's contributions were largely focused on the human side of the equation. Following are references to the passages from Engelbart's
early papers which highlight his
lab's orientation for Network Implications prior to and during
the formation of the ARPANET, still relevant to today's
Internet and World Wide Web, still not fully addressed.
The ARPANET Network Information Center was one tangible channel for infusing some of Engelbart's human-centered vision. His core research emphasized human process evolution equally important as the evolution of technology, stressing the importance of co-evolving the two in an integrated manner to achieve the best results. His concern from the beginning was that technology would race ahead of mankind's ability to cope. Watch in 1972 Dick Watson from Doug's lab and J.C.R. Licklider from ARPA voice these very concerns. Fast forward to the early 1990s when Doug reemerged with a Call to Action on the order of a Grand Challenge to spur proactive industry-government exploration into what it would take to boost our collective intelligence in business and society to the fullest extent possible. He proposed spinning up a number of specially-endowed pilot teams leveraging the most advanced modes of working together, enabled by highly evolved information technology and organizational processes. To speed things along he detailed what he saw to be the baseline requirements for the technology, which he called "open hyper document systems" (OHS) and which he pointed out as a serious matter were largely missing from then prevailing IT paradigm. It is important to note that most of these requirements are still largely unmet in any coherent way in today's web/IT paradigm, his Grand Challenge as yet unheeded (now referred to as "Engelbart's Unfinished Revolution" in contrast to the revolution(s) inspired by his work that did take hold).
Awards & Recognition 7
Press 8
More available at DEI Press Firsts:Networking
Footnotes: 10
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||